Analyze java dependencies with jQAssistant
by JohT
jQAssistant extracts meta data of java applications and writes them into Neo4j, a native graph database. This blog shows how these tools can be used to analyze java jar dependencies e.g. for version updates.
Table of Contents
- Table of Contents
- Fast lane
- Getting started
- Get familiar with the data
- Query the data
- Simple Data Refinement
- Manual Data Refinement
- Query refined data
- Summary
- Updates
- References
Fast lane
(Updated November 2023)
If you’d like to start with ready-to-use reports and a fully automated analysis pipeline then have a look at Code Graph Analysis Pipeline.
The installation of the newest version of the tools is done automatically including plugins and configuration. A huge amount of preexisting queries and reports also run fully automated and provide already a lot of insights about the code base.
If you on the other hand want to start small and learn step by step then continue reading.
Getting started
As described here, all you need to get started with jQAssistant is:
- Download it
- Scan for example the lib directory of jQAssistant itself using
bin\jqassistant.cmd scan -f lib(Windows) orbin/jqassistant.sh scan -f lib(Linux) - Start the web application to display and query the collected data using
bin\jqassistant.cmd server(Windows) orbin/jqassistant.sh server(Linux) - Open http://localhost:7474
- Sign in without user and password
- Click on the database symbol on the top left corner
Get familiar with the data
Neo4j is a graph database and uses Cypher as query language. For those who are used to SQL, “Comparing SQL with Cypher” might be a helpful guideline.
To get familiar with the data, use the database symbol on top left corner and select any of the node types to get some examples. Node symbols can be extended to show all relationships. Switching to table view shows all fields and their contents.
Query the data
Query class dependencies
Getting some dependencies between classes can be obtained with:
MATCH (dependent:Class)-[:DEPENDS_ON]->(source:Class)
RETURN source, dependent
LIMIT 25
Explanation
MATCH is somewhat comparable to SELECT in SQL.
The variables dependent and source are references to nodes of type Class.
Every class that depends on another class will be returned.
If there is no relationship between classes, if there is another type of relationship (like “implements”)
or if the dependency is in the opposite direction, then the nodes will be filtered out and will not be part of the result. Finally, all matching source and dependent class nodes will be returned, limited to at most 25.
Query Artifacts
Getting artifacts and types they require can be done using:
MATCH (source:Artifact)-[:REQUIRES]->(required:Type)
RETURN source, required
LIMIT 25
Explanation
Except for the types this query is pretty the same as the one above.
Troubleshooting
The next logical step would be MATCH (source:Artifact)-[:REQUIRES]->(required:Artifact).
But this returns no results. The reason for that becomes clear while reading the jQAssistant User Manual: The scanner does only provide “REQUIRES” between an artifact and a type,
not between two artifacts.
While analyzing jar files, each one is treated separately. Therefore, there will be no relationships between them. If two jars contain classes that depend on an external class, then the dependent class will appear multiple times. Caused by the way the jars are analyzed, there are multiple “Class” nodes with the same full qualified class name.
To summarize, the data is not yet ready to use for specific requirements.
Simple Data Refinement
(Updated December 2022)
The easiest way to close the gap between separately analyzed artifacts is provided by jQAssistant. The analyze command task can be configured to use -concepts to further enrich the nodes and their relationships. As described in Multiple jars with unique types (Stack Overflow), the classpath:Resolve Concept can be used to connect the types of the different artifacts. Furthermore, Concept dependency:Artifact adds the DEPENDS_ON relationship for Artifact nodes. Both of them combined into one command leads to:
bin/jqassistant.sh analyze -concepts classpath:Resolve dependency:Artifact
Further concepts and constraints can be found in the jQAssistant User Manual.
ⓘ Remember to stop the server before analyzing the data.
ⓘ
Note that Simple Data Refinement leads to a DEPENDS_ON relationship between Artifact nodes. In Manual Data Refinement below we introduce a REQUIRES relationship.
Manual Data Refinement
Compared to classical relational databases, graph databases like Neo4j are by nature very flexible
when it comes to relationships between nodes. The MERGE clause can be used to create a new
relationship if it hadn’t been there yet. This is done while querying, which makes it possible to refine the
data within a query and adapt it to the requirements.
Create relationships between Artifacts
The following query connects artifacts with required artifacts and classes with the same full qualified name (fqn). It returns a list of artifacts (jars) and their dependencies.
MATCH (sourceArtifact:Artifact)-[:REQUIRES]->(requiredType:Type)
,(dependencyType:Type)<-[:CONTAINS]-(dependencyArtifact:Artifact)
WHERE dependencyType.fqn = requiredType.fqn
MERGE (requiredType)-[:IS_SAME_AS]-(dependencyType)
MERGE (sourceArtifact)-[:REQUIRES]->(dependencyArtifact)
RETURN sourceArtifact.fileName, dependencyArtifact.fileName
Explanation
The query above leads to a warning message like “This query builds a cartesian product…”.
For every result in the first line all results of the second line will be returned.
Without a WHERE clause (or other filter options), this would lead to an enormous amount of data.
This is comparable to joins in SQL.
Since there is no relationship between types with the same full qualified name yet, they are queried
using two comma separated MATCH clauses. The WHERE class ensures that there will be
only one result in the second line for every result in the first line.
This is where MERGE comes into play. MERGE (requiredType)-[:IS_SAME_AS]-(dependencyType)
creates an undirected relationship between types with the same full qualified name,
so that later queries can be made without a potential cartesian product directly by querying the relationship.
It is also possible to add another MERGE clause to create one more relationship.
(sourceArtifact)-[:REQUIRES]->(dependencyArtifact) adds the expected but missing directional relationship
between an artifact and those artifacts it requires.
Query refined data
After adding relationships, artifacts that require other artifacts can easily be queried using:
MATCH (source:Artifact)-[:REQUIRES]->(required:Artifact)
RETURN source.fileName, required.fileName
With variable length relationships it is possible to query
in a recursive manner. Here is an example that returns all artifacts
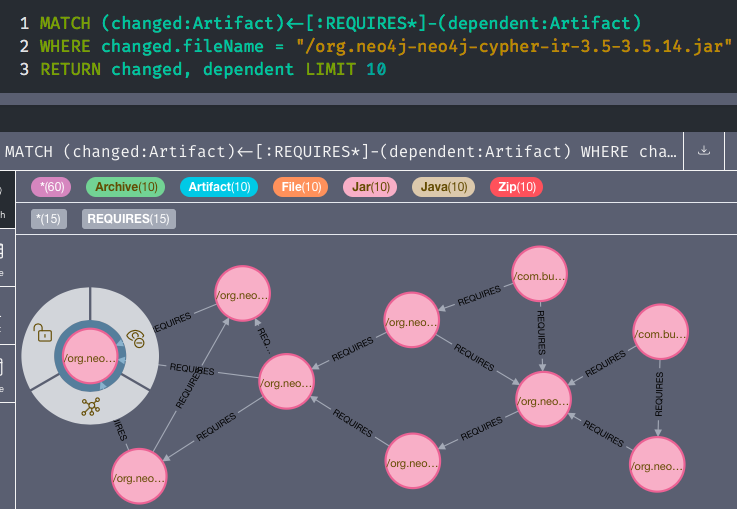
that could be affected by a version update of e.g. /org.neo4j-neo4j-cypher-ir-3.5-3.5.14.jar:
MATCH (changed:Artifact)<-[:REQUIRES*]-(dependent:Artifact)
WHERE changed.fileName STARTS WITH "/org.neo4j-neo4j-cypher-ir"
RETURN changed, dependent LIMIT 10
Neo4j Graph Result
Summary
Simple
(Updated December 2022)
Here are all steps using the simple data refinement in a nutshell:
- Download jQAssistant
- Scan a directory (e.g. “lib”) with jars:
bin/jqassistant.sh scan -f lib(POSIX) - Analyze with concepts:
bin/jqassistant.sh analyze -concepts classpath:Resolve dependency:Artifact(POSIX) - Start the web application:
bin/jqassistant.sh server(POSIX) - Open http://localhost:7474
- Sign in without user or password
-
Query the graph of all artifacts that would be affected by a version update of a given artifact:
MATCH (changed:Artifact)<-[:DEPENDS_ON*]-(dependent:Artifact) WHERE changed.fileName STARTS WITH "/org.neo4j-neo4j-cypher-ir" RETURN changed, dependent LIMIT 10
Manual
Here are all steps using the manual data refinement in a nutshell:
- Download jQAssistant
- Scan a directory (e.g. “lib”) with jars:
bin/jqassistant.sh scan -f lib(POSIX) - Start the web application:
bin/jqassistant.sh server(POSIX) - Open http://localhost:7474
- Sign in without user or password
-
Create relationships between artifacts and types and return a list of dependent jars with the following query:
MATCH (sourceArtifact:Artifact)-[:REQUIRES]->(requiredType:Type) ,(dependencyType:Type)<-[:CONTAINS]-(dependencyArtifact:Artifact) WHERE dependencyType.fqn = requiredType.fqn MERGE (requiredType)-[:IS_SAME_AS]-(dependencyType) MERGE (sourceArtifact)-[:REQUIRES]->(dependencyArtifact) RETURN sourceArtifact.fileName, dependencyArtifact.fileName -
Query the graph of all artifacts that would be affected by a version update of a given artifact:
MATCH (changed:Artifact)<-[:REQUIRES*]-(dependent:Artifact) WHERE changed.fileName STARTS WITH "/org.neo4j-neo4j-cypher-ir" RETURN changed, dependent LIMIT 10
Updates
- 2022-12-19: Add jQAssistant command for simple data refinement to Java JAR Dependencies Blog
- 2023-11-19: Reference Code Graph Analysis Pipeline
References
- About jQAssistant
- Getting started with jQAssistant
- Code Graph Analysis Pipeline
- Artifact Scanner of jQAssistant
- About Neo4j
- Neo4j Cypher Manual
- Comparing SQL with Cypher
- Query matching relationship with Neo4j
- Update relationships with Neo4j
- Variable length relationships with Neo4j
- Cartesian product
- Multiple jars with unique types (Stack Overflow)
- Concept classpath:Resolve
- Concept dependency:Artifact
- Rules provided by the jQAssistant Java Plugin
Hint: If you want to reach out to me without leaving a comment below, open a new discussion on GitHub.